Industrial Air Compressor Buyer's Guide: How to Choose the Perfect System in 2025
Industrial Air Compressor Buyer's Guide
Are you in the market for an industrial air compressor but feeling overwhelmed by the countless options and technical specifications? You're not alone. Choosing the right industrial air compressor is a significant investment that can impact your operations' efficiency and bottom line. The key is finding a system that perfectly matches your specific needs while ensuring long-term reliability and cost-effectiveness.
In this comprehensive 2025 buyer's guide, we'll walk you through everything you need to know about selecting the perfect industrial air compressor. From understanding different types to evaluating crucial factors like CFM, PSI, and horsepower ratings, we've got you covered.
Whether you're upgrading your existing system or purchasing your first industrial air compressor, this guide will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your operational requirements and budget.
Key Takeaways:
- Diverse Compressor Types: Understand the core differences between reciprocating (piston), rotary screw, and centrifugal compressors, as well as oil-lubricated vs. oil-free systems, to match them with specific applications and operational demands.
- Critical Technical Specifications: Prioritize pressure requirements (PSI), air flow (CFM), and power ratings (HP/kW) to ensure the compressor can adequately meet your current and future operational demands.
- Application-Specific Considerations: The optimal choice hinges on balancing factors like maintenance costs, energy efficiency, and long-term reliability against your unique industrial processes and tool requirements.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Look beyond the initial purchase price to consider long-term operating costs, including energy consumption, maintenance, and replacement parts.
- Professional Support is Paramount: Professional installation, ongoing support, and responsive customer service are crucial for optimal performance, system longevity, and peace of mind.
Understanding Air Compressors and Their Importance
Industrial air compressors have revolutionized modern manufacturing and industrial processes by harnessing the power of compressed air. These essential machines work by taking in ambient air and compressing it to higher pressures, storing this energy for various applications.
Evolution and Impact
The journey of air compressors dates back to the industrial revolution, where they played a crucial role in powering machinery and tools. Today, they've become the backbone of countless industries, from manufacturing to construction, automotive to pharmaceuticals.
How Air Compressors Work
At their core, air compressors operate on a simple yet effective principle. They draw in ambient air and compress it into a smaller volume, increasing its pressure. This compressed air is then stored in tanks, ready to be used when needed. The stored energy can power various tools and equipment, making it an incredibly versatile power source.
Benefits in Modern Industry
Modern industrial facilities rely heavily on compressed air systems for several reasons:
- Provides a clean and sustainable power source.
- Offers consistent and reliable performance.
- Enables efficient operation of pneumatic tools.
- Reduces overall operational costs.
- Ensures workplace safety through controlled power delivery.
Environmental Considerations
Air compressors represent an environmentally conscious choice for industrial power needs. Unlike many other power sources, they utilize the abundant ambient air, making them a sustainable option for businesses focusing on reducing their environmental impact.
Key Takeaway: Air compressors are fundamental industrial machines that transform ambient air into a powerful, versatile, and sustainable energy source for modern manufacturing and industrial applications.
Types of Industrial Air Compressors
Industrial air compressors come in various types, each designed for specific applications and requirements. Understanding these different types is crucial for making an informed purchase decision.
Reciprocating (Piston) Compressors
These traditional workhorses use pistons driven by a crankshaft to compress air. They're ideal for intermittent use and smaller operations. Piston compressors offer excellent reliability and are cost-effective for businesses with moderate air demands. They work by drawing air into a cylinder and compressing it through a reciprocating motion.
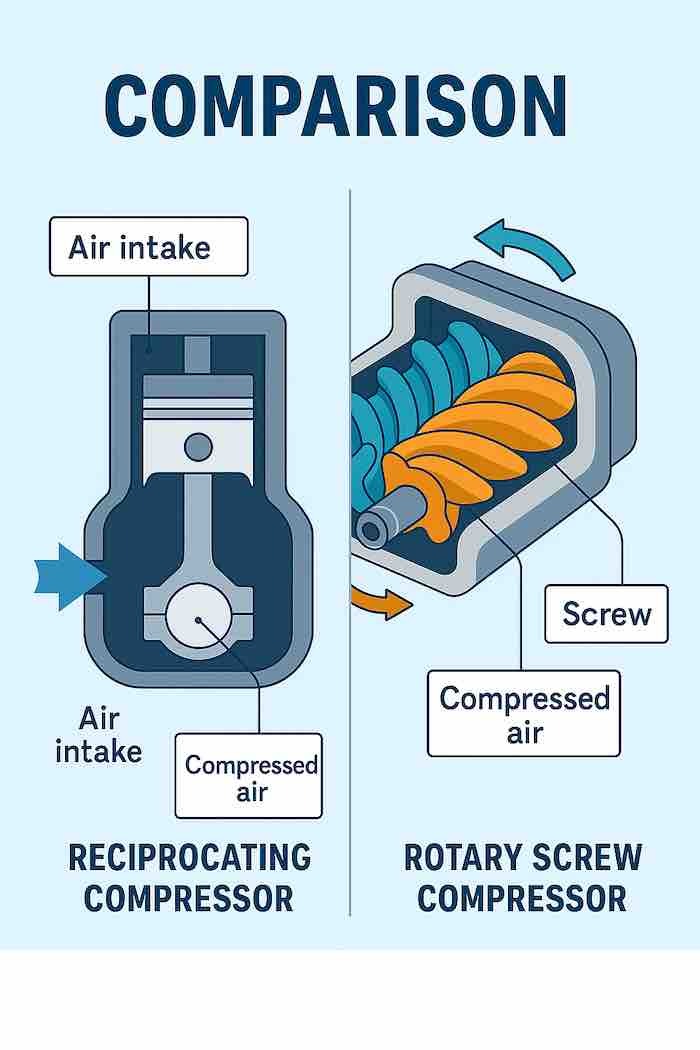
Rotary Screw Air Compressors
Perfect for continuous operation, rotary screw compressors use two meshing helical screws to compress air. They deliver consistent air flow and operate more quietly than piston compressors. These systems excel in environments requiring constant compressed air supply, like manufacturing facilities and large industrial operations.
Oil-Lubricated vs. Oil-Free Systems
Oil-lubricated compressors use oil for cooling and sealing, offering better efficiency and longer service life. However, oil-free systems are essential for applications requiring pure air, such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and electronics manufacturing. While oil-free units typically cost more initially, they eliminate the risk of oil contamination in the air supply.
Single-Stage vs. Two-Stage Compressors
Single-stage compressors compress air in one step, suitable for applications requiring up to 100 PSI. Two-stage compressors compress air twice, achieving higher pressures up to 175 PSI. They're more efficient for high-pressure applications and continuous use, though they come at a higher initial cost.
Key Takeaway: Industrial air compressors come in several main types—reciprocating, rotary screw, oil-lubricated/oil-free, and single/two-stage systems—each serving specific operational needs and applications.
Reciprocating Compressor Deep Dive
Reciprocating or piston compressors are among the most common types used in industrial settings. These machines work by using a crankshaft-driven piston that moves up and down within a cylinder to compress air.
How Reciprocating Compressors Work
The piston draws in ambient air during the downstroke through an inlet valve. As the piston moves upward, it compresses this air and forces it into a storage tank through a discharge valve. This simple yet effective mechanism makes piston compressors highly reliable for intermittent use applications.
Key Benefits
- Lower initial investment compared to other types.
- Easy maintenance and repair.
- Suitable for both small and large-scale operations.
- Excellent for applications requiring high pressure.
- Versatile performance across different pressure ranges.
Read Also;
Advanced Air Compressor Technologies: Innovations Driving Industrial Productivity and Sustainability
Common Applications
These compressors excel in environments where intermittent air supply is needed, such as:
- Auto repair shops
- Manufacturing facilities
- Construction sites
- Small industrial operations
- Woodworking shops
However, reciprocating compressors tend to be louder and generate more heat than other types. They also require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Key Takeaway: Reciprocating compressors offer a cost-effective and reliable solution for industrial applications requiring intermittent compressed air supply, despite their higher noise levels and maintenance needs.
Rotary Screw Air Compressor Deep Dive
Rotary screw air compressors are highly efficient machines designed for continuous operation in industrial settings. These compressors use two rotating helical screws to compress air, delivering a steady and reliable flow of compressed air.
Key Features of Rotary Screw Compressors
- Continuous duty operation capability.
- Lower operating temperatures.
- Quieter operation compared to reciprocating compressors.
- Better energy efficiency at full load.
- Longer service life due to fewer moving parts.
Benefits for Industrial Applications
These systems excel in environments requiring constant air supply. The lubricated rotary screw type compressor provides superior performance for manufacturing facilities, automotive plants, and large-scale operations where consistent air pressure is crucial. The design allows for better thermal management, reducing the risk of overheating during extended use. This makes them ideal for facilities operating multiple shifts or requiring 24/7 operation.
Energy Efficiency Advantages
Modern rotary screw compressors often come equipped with variable speed drives (VSD), allowing them to adjust output based on demand. This feature significantly reduces energy consumption during periods of lower demand, making them more cost-effective in the long run.
Key Takeaway: Rotary screw air compressors offer reliable, efficient, and continuous compressed air supply, making them ideal for industrial applications requiring consistent performance and extended operation periods.
Oil-Lubricated vs. Oil-Free Systems Deep Dive
The choice between oil-lubricated and oil-free air compressors is critical and depends entirely on your application's air purity requirements.
Oil-Lubricated Systems
Oil-lubricated compressors inject oil into the compression chamber to reduce friction, provide cooling, and create an airtight seal. These systems are highly efficient and typically have a longer lifespan due to reduced wear and tear on components. They're ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications where air purity isn't critical.
Key Benefits of Oil-Lubricated Systems:
- Enhanced durability and longevity.
- Better heat dissipation.
- More cost-effective operation.
- Higher efficiency ratings.
- Lower maintenance frequency for general use.
Oil-Free Systems
Oil-free systems, on the other hand, use specialized coatings and materials to prevent metal-to-metal contact without oil. These systems are essential in industries requiring pristine air quality, such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and electronics manufacturing. While they typically have higher initial costs, they eliminate the risk of oil contamination in the compressed air supply.
Applications Where Oil-Free is Crucial:
- Medical facilities
- Clean room operations
- Food packaging
- Semiconductor manufacturing
- Pharmaceutical production
Key Takeaway: Choose oil-lubricated systems for general industrial use and cost-efficiency where minimal oil carryover is acceptable, while opting for oil-free systems when air purity is paramount for your specific application.
Helical Screws of Rotary Air compressors
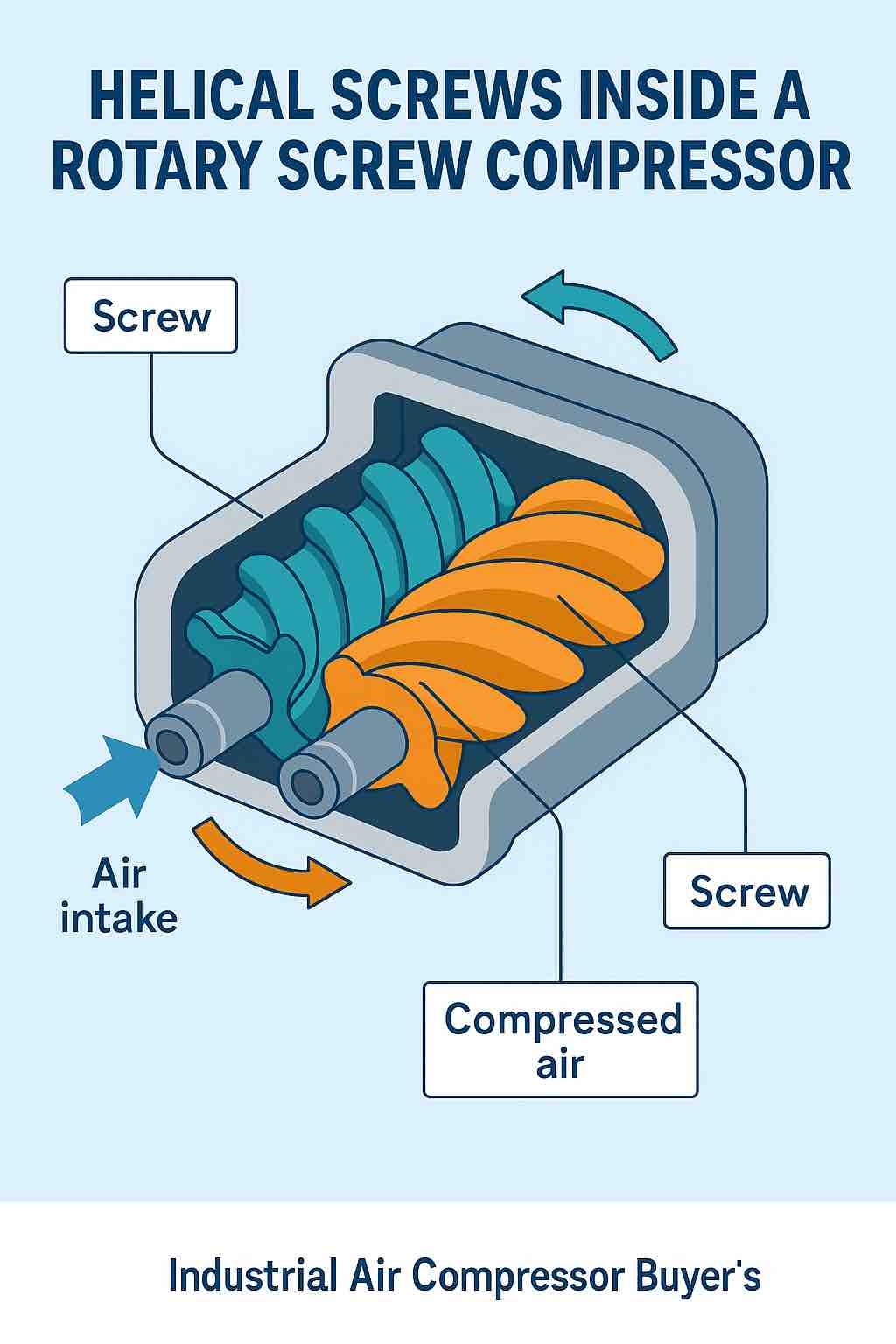
Single-Stage vs. Two-Stage Compressors Deep Dive
The number of compression stages impacts a compressor's pressure output, efficiency, and suitability for different applications.
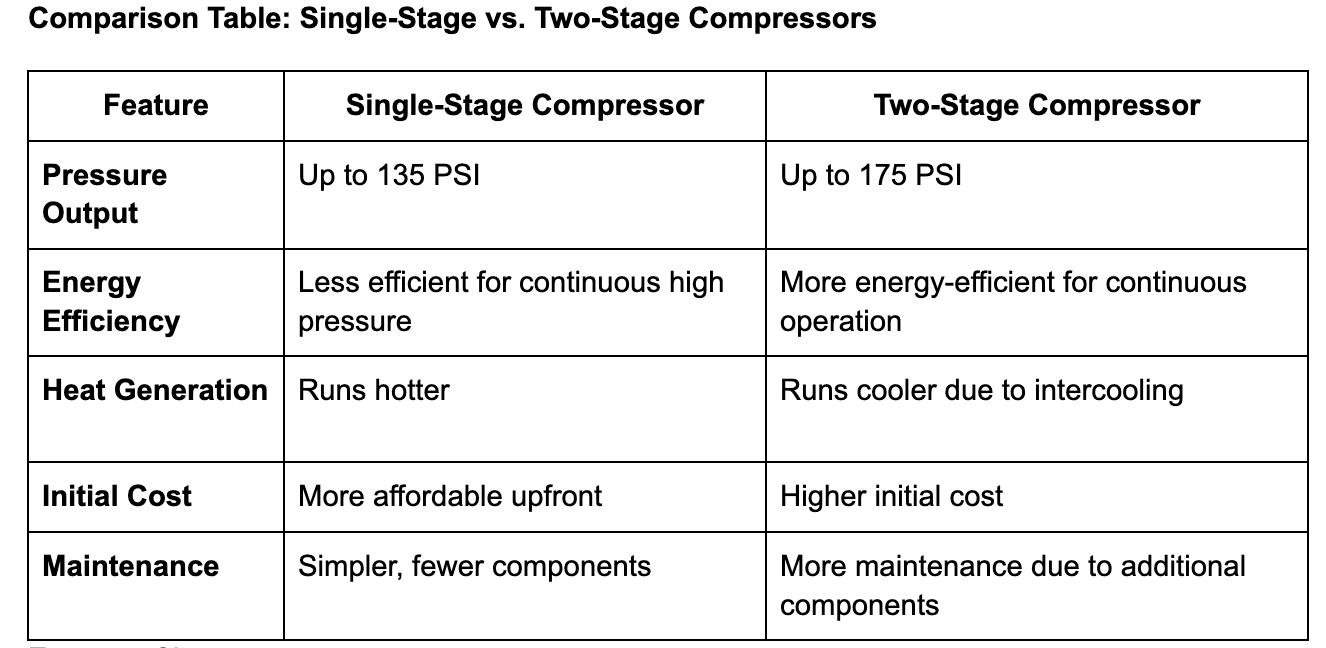
Single-Stage Compressors
Single-stage compressors complete the compression process in one step, making them ideal for smaller operations and intermittent use. These units are more compact and cost-effective, typically operating at pressures up to 135 PSI.
Two-Stage Compressors
Two-stage compressors, on the other hand, compress air in two distinct phases. The first stage compresses air to an intermediate pressure, while the second stage further compresses it to reach higher pressures up to 175 PSI. This design includes an intercooler between stages to reduce air temperature and improve efficiency.
Best Applications
Single-stage compressors work well for:
- Small workshops
- Light industrial use
- Intermittent operations
- Basic pneumatic tools
Two-stage compressors are ideal for:
- Manufacturing facilities
- Heavy-duty applications
- Continuous operations
- High-pressure requirements
Key Takeaway: Choose single-stage compressors for basic, intermittent use and two-stage systems for heavy-duty, continuous operations requiring higher pressure outputs and greater efficiency.
Technical Specifications and Measurements
The technical specifications of an industrial air compressor play a crucial role in determining its performance and suitability for your specific needs. Understanding these measurements helps ensure you select a system that meets your operational requirements.
Pressure (PSI/Bar)
Pressure, measured in Pounds per Square Inch (PSI) or Bar, indicates the force at which air is compressed. Most industrial applications require pressures between 100-175 PSI. Higher pressure ratings don't necessarily mean better performance—it's essential to match the pressure to your specific application requirements. Always factor in a safety margin (10-15 PSI) above your tools' requirements to account for pressure drops in air lines and ensure consistent performance.
Air Flow Rate (CFM)
Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM) measures the volume of air flow the compressor can deliver. This specification is particularly critical as it determines the compressor's ability to meet your air demand. A general rule of thumb is to calculate your total CFM needs (summing all tools that might run simultaneously) and add 25-30% for future expansion or unexpected demands, as well as accounting for potential air leaks.
Power Rating (HP/kW)
Horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW) indicates the compressor's power capacity. Industrial compressors typically range from 5 HP to 500 HP. The power rating directly affects:
- Compression capability
- Operating efficiency
- Energy consumption
- Overall performance
Voltage Requirements
Most industrial compressors operate on:
- Single-phase (230V) for smaller units.
- Three-phase (208-230V/460V) for larger systems.
Always verify your facility's power supply matches the compressor's requirements to ensure proper operation and prevent electrical issues.
Key Takeaway: Technical specifications like pressure (PSI), air flow (CFM), power rating (HP), and voltage requirements form the foundation for selecting an appropriately sized industrial air compressor system.
Essential Features to Consider
When selecting an industrial air compressor, several essential features demand careful consideration to ensure optimal performance and longevity. These key elements can significantly impact your system's efficiency and reliability.
Cooling System Design
A robust cooling system is crucial for maintaining optimal operating temperatures. Modern industrial compressors typically feature either air-cooled or water-cooled systems. Air-cooled systems are more common and require less maintenance, while water-cooled systems offer superior temperature control for high-demand applications.
Control Systems
Advanced control systems help optimize performance and prevent system failures. Look for features like:
- Automatic start/stop functionality
- Digital pressure control
- Remote monitoring capabilities
- Predictive maintenance alerts
- Load/unload controls
Safety Features
Essential safety components protect both equipment and operators:
- Emergency shutdown systems
- Thermal overload protection
- High-temperature shutdown
- Low-oil level sensors
- Belt guards and protective covers
Noise Reduction
Modern compressors incorporate various noise reduction features:
- Sound-attenuating enclosures
- Anti-vibration mounts
- Specialized intake silencers
- Insulated compressor rooms (for extreme cases)
Storage Capacity (Air Receiver Tank)
The air receiver tank size matters significantly:
- Larger tanks provide better pressure stability.
- Helps manage peak demand periods.
- Reduces compressor cycling, extending equipment life.
- Improves system efficiency.
Moisture Management
Effective moisture control is vital for system longevity and preventing damage to downstream equipment and products. A comprehensive system includes:
- Automatic drain valves
- Air dryers (refrigerated or desiccant)
- Moisture separators
- Multi-stage filtration systems
- Condensate management solutions
Key Takeaway: Essential features in industrial air compressors encompass robust cooling systems, intelligent controls, comprehensive safety mechanisms, noise reduction, adequate storage capacity, and effective moisture management—all crucial for optimal performance and reliability.
Readers Like : Optimizing Your Industrial Air Compressor: Maximizing Efficiency & Minimizing Costs
Application-Specific Requirements
Industrial air compressors serve diverse purposes across various industries, each with unique requirements and specifications. Understanding these application-specific needs is crucial for selecting the right system that aligns with your operational demands.
Industrial Applications Overview
- Manufacturing Facilities: Often require high-capacity, continuous-duty compressors for powering production lines, robotics, and automated systems (e.g., rotary screw).
- Automotive Plants: Compressed air drives assembly tools, paint spraying equipment, and testing instruments. Air quality is important for paint finishes.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Demands oil-free systems to maintain product purity and meet strict hygiene standards.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Requires the highest air quality standards (ISO 8573-1 Class 0) for critical processes and cleanroom environments.
- Metal Fabrication Shops: Typically need robust systems capable of handling multiple pneumatic tools simultaneously, requiring higher CFM ratings and consistent pressure.
- Electronics Manufacturing: Requires specialized systems with precise humidity control and contamination prevention features.
Tool Requirements
Different pneumatic tools have varying air consumption needs. It's crucial to list all tools you intend to use and their individual CFM and PSI requirements.
Common Air Tools and Their Typical Requirements:
- Impact Wrenches: 4-5 CFM at 90 PSI
- Paint Sprayers: 6-9 CFM at 40 PSI (often continuous use)
- Sanders: 6-9 CFM at 90 PSI (continuous use)
- Air Hammers: 2-4 CFM at 90 PSI
- Pneumatic Drills: 3-6 CFM at 90 PSI
- Pneumatic Cylinders: Varies greatly by size and cycle rate.
Calculating Total Tool Demand:
To determine your total air requirement:
- List all pneumatic tools you'll use simultaneously during peak operation.
- Add up their individual CFM requirements.
- Multiply the total by 1.25 to account for system losses, potential leaks, and a safety buffer for future expansion.
Image Location: Consider an infographic showing common pneumatic tools with their typical CFM and PSI requirements.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Energy efficiency has become a crucial factor in industrial air compressor selection, especially with rising energy costs and environmental concerns. Modern air compressors incorporate new technology and innovative features to maximize energy savings while maintaining optimal performance.
- Variable Speed Drive (VSD) Technology: VSDs automatically adjust the motor speed based on air demand, significantly reducing energy consumption (up to 35%) during periods of low or fluctuating usage.
- Heat Recovery Systems: These systems capture and repurpose waste heat generated during compression (up to 94% of input energy can be recovered), which can be used for space heating, water heating, or other industrial processes.
- Smart Controls and Monitoring: Intelligent control systems monitor and optimize energy usage patterns, provide real-time data, and alert operators to potential efficiency issues.
- Energy-Saving Operating Practices: Regular maintenance, leak detection and repair programs, proper sizing, and operating at the lowest effective pressure all contribute to significant energy savings.
Key Takeaway: Application-specific requirements vary across industries, from critical air purity needs and precise tool specifications to significant energy efficiency considerations, making it essential to understand your unique operational demands when selecting an industrial air compressor.
Selection Criteria for the Perfect System
Selecting the perfect industrial air compressor requires careful consideration of multiple factors to ensure optimal performance and long-term value. A systematic approach to evaluation will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your operational needs.
Assessing Your Specific Needs
- Current Air Usage: Evaluate your current compressed air consumption. Calculate the total CFM requirements by listing all pneumatic tools and equipment you use, considering both regular operations and peak demand periods.
- Future Growth Plans: Look beyond immediate needs and factor in potential expansion. Choose a compressor that can accommodate future growth without requiring immediate replacement.
- Environmental Factors: Consider your facility's environmental conditions: ambient temperature ranges, available space for installation, ventilation requirements, and noise level restrictions.
- Operating Schedule: Determine your typical operating patterns: daily runtime hours, peak usage periods, continuous vs. intermittent use, and number of shifts. This helps select a compressor with the right duty cycle and capacity.
Maintenance and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Look beyond the initial purchase price and evaluate the total cost of ownership, which can be significantly higher than the upfront investment.
- Energy Consumption Costs: This is often the largest component of TCO (up to 75%). Factor in the energy efficiency ratings and running hours to estimate your monthly power expenses. VSD compressors can offer substantial savings here.
- Regular Maintenance Expenses: Plan for routine tasks (e.g., oil checks, filter cleaning weekly/monthly) and major maintenance (e.g., oil changes, filter replacements quarterly/annually).
- Replacement Parts Availability: Budget for routine replacement parts (air filters, oil filters, separator elements, lubricants, belts) and consider their availability.
- Service Contracts: Evaluate service contracts that include regular maintenance visits, emergency repair coverage, and priority response times to minimize downtime.
Customer Support and Reviews
Research manufacturer reputation and after-sales support. Look for:
- Responsive Customer Service: Timely and effective communication for inquiries and issues.
- Local Dealer Network: Ensures proximity for service and parts.
- Available Technical Support: Expertise to resolve complex problems.
- Spare Parts Availability: Crucial for minimizing downtime during repairs.
- Training Programs: For your staff on operation and basic maintenance.
- Emergency Repair Services: Critical for avoiding prolonged operational halts.
Read customer reviews and case studies from similar industries. This provides valuable insights into real-world performance, reliability, and the quality of support.
Key Takeaway: A successful air compressor selection combines thorough needs assessment, comprehensive total cost of ownership analysis (including energy and maintenance), and reliable customer support infrastructure to ensure optimal long-term performance and value.
Professional Installation and Support
Professional installation and ongoing support are crucial investments when acquiring an industrial air compressor system. A properly installed system ensures optimal performance, longevity, and safety while minimizing operational issues.
Installation Requirements
A professional installation team will assess your facility's layout, power availability, and ventilation needs. They'll ensure proper mounting, electrical connections, and adequate airflow around the unit. This helps prevent overheating and maintains system efficiency.
The installation process typically includes:
- Foundation preparation and mounting.
- Electrical system setup, ensuring correct voltage and wiring.
- Compressed air piping installation, including proper sizing and routing to minimize pressure drops.
- Ventilation system configuration to dissipate heat effectively.
- Implementation of all necessary safety features.
Ongoing Support Services
Regular maintenance and reliable support services are essential for keeping your air compressor running smoothly and maximizing its lifespan. Professional support typically includes:
- 24/7 emergency assistance to address unexpected breakdowns promptly.
- Scheduled maintenance visits to perform routine checks and preventative tasks.
- Performance monitoring to identify inefficiencies or potential issues early.
- Parts replacement services with genuine components.
- System optimization recommendations to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Training and Documentation
Most professional installers provide comprehensive training for your staff on:
- Basic operation procedures and daily checks.
- Safety protocols and emergency shutdown procedures.
- Routine maintenance tasks your team can perform.
- Troubleshooting common issues.
They also supply detailed documentation, including operation manuals, maintenance schedules, and warranty information for extensive use of the system.
Key Takeaway: Professional installation and ongoing support services are vital investments that ensure optimal performance, safety, and longevity of your industrial air compressor system while providing peace of mind through expert assistance and comprehensive training.
Conclusion
Selecting the perfect industrial air compressor is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your operations. By meticulously considering factors such as compressor types, detailed technical specifications (PSI, CFM, HP), application-specific requirements (air purity, tool needs), and the total cost of ownership (energy efficiency, maintenance), you can make an informed choice that aligns perfectly with your needs and budget. Remember to assess duty cycles, air quality requirements, and invest in energy-efficient features to maximize your investment.
As you embark on this journey, don't hesitate to seek professional advice and support from experienced suppliers. The right air compressor can revolutionize your industrial processes, boost productivity, and drive long-term cost savings. Take the time to evaluate your options carefully, and never compromise on quality or reliable performance.
Ready to transform your operations with the ideal industrial air compressor? Explore our range of top-quality systems and expert consultation services today. Your perfect compressed air solution is just a click away!
Call to Action: Contact Tend Industrial Supplies at sales@tendsupplies.com for expert consultation and to explore our range of industrial air compressors perfectly suited for your needs.
Related Articles
Understanding the Right Size of Air Compressor for Your Pneumatic Air Tools in 2024: Dive deeper into calculating your precise CFM needs and matching them to your specific pneumatic tools for optimal performance.
Decoding CFM: Why It Matters in Air Compressor Performance: A detailed look at Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM) and its critical role in ensuring your compressor can keep up with demand.
How to Choose the Right Air Compressor Size: Get a general overview and practical tips on sizing your compressor for various applications, whether large or small.
2024's Leading Air Compressors: Comprehensive Reviews and Buyers Guide: While our guide looks to 2025, this article provides a solid foundation of top models and buyer insights from the current year.
Maximizing Performance: How to Choose the Right Air Compressor for Your Impact Wrench: If impact wrenches are a primary tool, this guide offers specialized advice to ensure powerful and efficient operation.
Choosing the Right Air Compressor for Painting Projects: This article delves into the unique CFM and air quality needs for those specifically requiring air for painting.
FAQs
1. What is the average lifespan of an industrial air compressor?
The average lifespan of a well-maintained industrial air compressor is typically 10-15 years. However, this can vary significantly based on usage patterns, the quality of maintenance performed, and the specific operating conditions (e.g., ambient temperature, dust levels). Regular servicing according to manufacturer guidelines and proactive issue resolution can extend the lifespan considerably.
2. How often should I perform maintenance on my industrial air compressor?
Maintenance frequency depends on the compressor type, usage intensity, and operating environment. Generally, daily visual inspections are essential (e.g., checking for leaks, unusual noises). Basic maintenance tasks like checking oil levels, cleaning air filters, and draining moisture should be performed weekly or monthly. Major maintenance, including oil changes, filter replacements, and system checks, should be scheduled quarterly or bi-annually, as per manufacturer recommendations.
3. Can I upgrade my existing air compressor system instead of buying a new one?
Yes, in many cases, existing air compressor systems can be significantly upgraded to improve efficiency and performance, often at a lower cost than purchasing a completely new unit. Common upgrades include installing Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) to optimize energy consumption, enhancing air treatment systems (e.g., adding dryers or better filters), or implementing advanced control systems for smarter operation and monitoring.
4. What are the signs that my industrial air compressor needs replacement?
Key indicators that your industrial air compressor might need replacement include frequent breakdowns and increasing repair costs, a noticeable decrease in performance (e.g., inability to maintain required air pressure or CFM), excessive energy consumption despite maintenance, unusual noises or vibrations, or when repair costs exceed 50% of the cost of a new, more efficient unit. Technological obsolescence and difficulty in sourcing parts for older models are also important factors.
5. How much space do I need to install an industrial air compressor?
The required space depends significantly on the compressor's size, type, and specific configuration (e.g., with or without integrated dryer and tank). As a general rule, you should allow for at least 3 feet of clearance on all sides of the unit for proper ventilation, heat dissipation, and ease of maintenance access. Additional space might be needed for external air treatment equipment, larger air receiver tanks, and dedicated compressor room infrastructure. It's always best to consult with a professional installer for precise space requirements based on your chosen model.









