Air Compressor Troubleshooting: Diagnosing and Fixing Common Industrial Issues for Peak Uptime
In the fast-paced world of industrial operations, where pneumatic systems are the lifeblood of production, an air compressor malfunction isn't just an inconvenience, it's a critical threat to uptime, efficiency, and the bottom line. Despite implementing robust maintenance routines (as highlighted in our 10 Essential Air Compressor Maintenance Tips), issues can sometimes arise. Knowing how to swiftly diagnose and effectively resolve common air compressor problems is paramount for minimizing downtime and maintaining uninterrupted productivity.
This comprehensive guide serves as your go-to resource for industrial air compressor troubleshooting. We'll equip you with the knowledge and practical steps to identify the root causes of typical malfunctions, from unexpected shutdowns and pressure drops to excessive noise and oil carryover. Our expert insights will empower your team to perform crucial diagnostics and implement effective fixes, preventing minor glitches from escalating into costly repairs or system failures.
Whether you're a seasoned maintenance professional or managing a facility reliant on compressed air, understanding these troubleshooting techniques will significantly enhance your operational resilience, reduce service calls, and ensure your industrial air compressor system maintains peak uptime.
Key Takeaways:
- Systematic Diagnostic Approach: Adopt a methodical troubleshooting process, starting with fundamental checks (power, air supply, controls) before delving into more complex component diagnostics.
- Pressure is Paramount: Fluctuating or insufficient pressure is a common indicator of underlying issues, often pointing to leaks, clogged filters, or improper settings.
- Sound and Vibration as Clues: Unusual noises (knocking, squealing) and excessive vibration are critical warning signs that require immediate investigation to prevent catastrophic component failure.
- Air Quality Matters: Issues like oil carryover or excessive moisture directly impact downstream equipment and product quality, necessitating prompt attention to filters, dryers, and separators.
- Leverage Manufacturer Resources & Professionals: Always consult your compressor's manual and don't hesitate to seek professional service for complex, persistent, or safety-critical issues.
Understanding the Troubleshooting Mindset: Beyond Maintenance
While diligent maintenance (as detailed in our 10 Essential Air Compressor Maintenance Tips) significantly reduces the likelihood of issues, even the best-kept machinery can encounter unexpected problems. Troubleshooting is the art and science of diagnosing these issues, a detective process that requires a systematic approach.
The Importance of Rapid Diagnosis
In industrial settings, every minute of downtime is a minute of lost production and revenue. Rapid, accurate diagnosis is crucial for:
- Minimizing Downtime: Quickly identifying the problem allows for swift resolution and restoration of operations.
- Preventing Escalation: Addressing minor issues before they lead to catastrophic component failures and more expensive repairs.
- Ensuring Safety: Diagnosing and fixing problems related to pressure, heat, or electrical faults protects personnel and assets.
- Maintaining Efficiency: Resolving issues that cause the compressor to work harder, thus preventing increased energy consumption.
The Troubleshooting Process: A Logical Flow
A successful troubleshooting strategy typically follows a logical, step-by-step process:
- Observe and Gather Information: What are the symptoms? When did it start? Were there any recent changes? Check all gauges and indicators.
- Verify Basics: Rule out simple, common causes first (power, air supply, emergency stops).
- Isolate the Problem: Determine which component or system is likely at fault.
- Test and Confirm: Perform specific checks or tests to confirm your diagnosis.
- Implement Solution: Apply the appropriate fix.
- Verify Repair: Ensure the system operates correctly after the fix.
- Document: Record the problem, cause, and solution for future reference.
Key Takeaway: Adopting a systematic and logical troubleshooting mindset is paramount for quickly diagnosing air compressor malfunctions, thereby minimizing costly downtime, preventing escalation of issues, enhancing safety, and maintaining operational efficiency.
Common Industrial Air Compressor Issues and Solutions
Let's delve into the most frequent problems encountered with industrial air compressors and provide actionable steps to diagnose and resolve them.
Issue 1: Compressor Not Starting or Cycling On/Off Frequently

This is a common and immediate concern, as a non-starting or erratic compressor means no compressed air.
Possible Causes:
- No Power: Loose electrical connections, tripped circuit breaker, blown fuse, motor overload.
- Emergency Stop Engaged: Safety button pressed.
- Pressure Switch Malfunction: Faulty switch or incorrect settings.
- Motor Overheating: Thermal overload triggered.
- Low Oil Level (for oil-lubricated): Safety shutdown due to insufficient lubrication.
- Drain Valve Stuck Open: Prevents pressure buildup.
- Control System Error: Software or sensor issue.
Troubleshooting Steps & Solutions:
- Check Power Supply: Verify circuit breakers, fuses, and all electrical connections. Ensure the voltage matches compressor requirements.
- Reset Emergency Stop: Confirm the emergency stop button is disengaged.
- Inspect Pressure Switch: Check settings; if adjustable, ensure they are correct. Test switch functionality if possible (consult manual).
- Allow Motor to Cool: If thermal overload tripped, let the motor cool down. Check for proper ventilation around the compressor.
- Check Oil Level: For oil-lubricated units, verify oil level and add if low. (See our 10 Essential Air Compressor Maintenance Tips).
- Check Drain Valves: Ensure all manual and automatic drain valves are properly closed and not stuck open.
- Consult Control Panel: Look for error codes or messages on the control panel, then refer to the manual for specific interpretations.
Issue 2: Insufficient or Fluctuating Air Pressure
This problem directly impacts pneumatic tool performance and process efficiency.
| Symptom | Likely Cause(s) | Quick Fix / Check |
| Low Overall Pressure | Leaks, Clogged Filter, Undersized Compressor | Leak detection, filter change, assess sizing. |
| Pressure Drops at Tool | Tool Demand > Supply, Undersized Hose/Fittings | Check tool CFM, upgrade hose, regulate pressure. |
| Compressor Runs Constantly | High Demand, Large Leaks, Check Valve Issue | Reduce demand, fix leaks, professional check. |
Possible Causes:
- Air Leaks: Most common cause.
- Clogged Air Filter: Restricting intake.
- Excessive Air Demand: System consumption exceeds compressor output.
- Worn Compressor Components: Air end wear, piston rings, valves.
- Pressure Regulator Malfunction: Faulty or improperly set.
- Undersized Piping: Creating significant pressure drops.
- Improperly Sized Compressor: Not enough CFM for demand.
Troubleshooting Steps & Solutions:
- Detect and Repair Air Leaks: Use an ultrasonic leak detector or soapy water solution to find and fix all leaks in the piping network, hoses, fittings, and tools. (Refer to our guide on Optimizing Your Industrial Air Compressor: Maximizing Efficiency & Minimizing Costs for detailed leak detection strategies).
- Inspect and Replace Air Filter: Check the intake air filter for dirt and debris. Clean or replace it if clogged.
- Assess Air Demand: Monitor peak air consumption. If demand consistently exceeds the compressor's CFM rating, consider adding capacity or implementing a Variable Speed Drive (VSD) to match demand.
- Check Pressure Regulator: Verify the regulator setting is correct. If it's faulty, replace it.
- Inspect Piping: Ensure piping is correctly sized for your air flow. Undersized pipes cause significant pressure drops. Consider a loop system for better distribution.
- Evaluate Compressor Sizing: If the compressor consistently runs at 100% duty cycle and still can't meet demand, it may be undersized. (Our Understanding the Right Size of Air Compressor for Your Pneumatic Air Tools in 2024 article can help).
Issue 3: Excessive Noise or Vibration
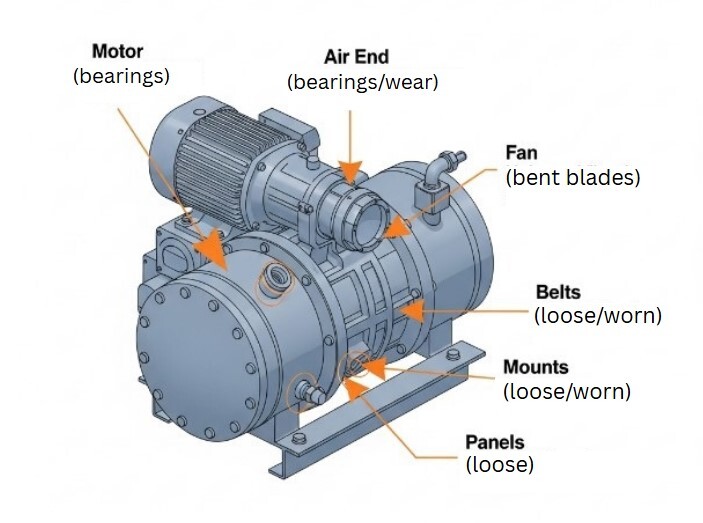
An air compressor is never silent, but sudden increases in noise or vibration are red flags.
Possible Causes:
- Loose Components: Belts, pulleys, motor mounts, panels.
- Worn Bearings: In motor, air end, or other rotating parts.
- Improper Lubrication: Lack of oil, incorrect oil type.
- Unbalanced Components: Fan, motor, or air end.
- Inlet Filter Clogged: Causes motor strain and noise.
- Damaged Fan/Motor: Bent fan blades, motor issues.
- Resonance/Mounting Issues: Compressor not properly leveled or isolated.
Troubleshooting Steps & Solutions:
- Tighten Loose Components: Inspect all external panels, bolts, and mounting hardware. For belt-driven units, check belt tension.
- Check Lubrication: Ensure oil level is correct and oil quality is good. (Refer to our Air Compressor Maintenance Tips for oil management).
- Inspect Air Filter: A clogged filter can make the compressor work harder and be noisier. Clean or replace.
- Examine Cooling Fan: Look for bent blades or obstructions.
- Assess Mounting: Ensure the compressor is level and on a stable, vibration-dampening surface. Check anti-vibration pads if installed.
- Listen and Isolate: Try to pinpoint the source of the noise (e.g., motor, air end, fan). If it sounds like grinding or screeching from internal components, shut down immediately and call a professional.
- Consider Quiet Models: If noise is a consistent concern, especially for smaller workshops, explore Quiet Air Compressors: The Best Options for Home Garages and Small Workshops.
Issue 4: Excessive Oil Carryover or Moisture in Air Lines
| Symptom | Likely Cause(s) | Component to Check |
| Oil in Air Lines | Overfilled oil, faulty oil separator, worn piston rings | Oil Level, Oil Separator, Cylinder/Piston |
| Water in Air Lines | No/faulty air dryer, stuck automatic drain, aftercooler issue | Air Dryer, Automatic Drains, Aftercooler |
| Dusty/Dirty Air | Clogged air intake filter, damaged piping | Air Intake Filter, Piping Integrity |
Contaminated air is detrimental to tools and products.
Possible Causes (Oil Carryover):
- Overfilled Oil Reservoir: Most common.
- Clogged or Faulty Oil Separator: For rotary screw units.
- Worn Piston Rings/Cylinder Walls: For reciprocating units.
- Incorrect Oil Type: Too thin, wrong additives.
- High Operating Temperature: Causes oil to vaporize more.
Possible Causes (Moisture):
- Ineffective or No Air Dryer: Humid air condenses without proper removal.
- Automatic Drains Malfunctioning: Condensate not being purged.
- Improper Aftercooler Function: Not cooling air sufficiently.
- High Ambient Humidity: Overwhelming the drying system.
Troubleshooting Steps & Solutions:
- Check Oil Level (Carryover): Ensure oil is at the correct level, not overfilled.
- Inspect/Replace Oil Separator (Carryover): For rotary screw compressors, a clogged or damaged separator needs replacement.
- Verify Oil Type (Carryover): Confirm you're using the correct compressor oil as per manufacturer specs.
- Check Aftercooler Function (Moisture): Ensure it's cooling the compressed air efficiently.
- Inspect/Maintain Air Dryer (Moisture): Verify the dryer is operational. Check desiccant if applicable. If you don't have one and moisture is critical, consider installing one. (Refer to our Advanced Air Compressor Technologies for dryer advancements).
- Test Automatic Drains (Moisture): Ensure automatic drain valves on the receiver tank and dryer/filters are cycling and not clogged.
- Address High Temperature: Ensure proper ventilation and clean cooling fins to prevent overheating, which contributes to oil vaporization and moisture. (See "Control Temperature and Pressure" in our maintenance guide).
Issue 5: Compressor Overheating

Overheating is a serious issue that can lead to premature component failure and safety hazards.
Possible Causes:
- Insufficient Ventilation: Poor airflow around the compressor.
- Dirty Cooling Fins/Coolers: Blocked heat dissipation.
- Low Oil Level or Poor Oil Quality: Inadequate lubrication and cooling.
- High Ambient Temperature: Room is too hot.
- Clogged Air Filter: Forces compressor to work harder.
- Motor Overload: Compressor is undersized for demand.
- Faulty Thermostat or Temperature Sensor: Incorrect readings.
Troubleshooting Steps & Solutions:
- Improve Ventilation: Ensure the compressor room has adequate airflow. Clear any obstructions around the unit. Consider exhaust fans or ducting.
- Clean Coolers: Regularly clean cooling fins, intercoolers, and aftercoolers to remove dust, debris, and oil film.
- Check Oil System: Verify correct oil level and quality. Change oil if contaminated or degraded. (See "Maintain Proper Oil Management" in our 10 Essential Air Compressor Maintenance Tips).
- Monitor Room Temperature: Ensure the ambient temperature in the compressor room is within the recommended range (typically 50-85°F).
- Inspect Air Filter: A dirty air filter increases motor strain and heat. Clean or replace.
- Assess Load: If the compressor is constantly running at full load or beyond its capacity, it might be undersized. (Our guide on Understanding the Right Size of Air Compressor for Your Pneumatic Air Tools in 2024 can help with sizing).
- Consult Professional: If overheating persists after these checks, it may indicate a faulty thermostat, temperature sensor, or internal air end issue requiring professional diagnosis.
When to Call a Professional: Knowing Your Limits
While this guide empowers you with significant troubleshooting capabilities, it's crucial to recognize when a problem extends beyond DIY fixes and requires expert intervention. Calling a professional service technician from Tend Industrial Supplies is advisable when:
- Safety Concerns: Any issue involving exposed electrical wiring, extreme pressure fluctuations, or strong burning smells.
- Complex Internal Failures: Suspected issues with the air end, motor bearings, or major electrical components.
- Persistent Problems: Issues that reoccur despite your best troubleshooting efforts.
- Warranty Requirements: Many warranties mandate professional service for specific repairs or maintenance milestones.
- Specialized Tools/Knowledge: Problems requiring specialized diagnostic equipment or in-depth technical knowledge of complex compressor models.
- Lack of Internal Expertise: If your team lacks the training or experience for a particular repair.
Remember: Timely professional intervention can often prevent a small issue from becoming a catastrophic failure, ultimately saving you money and downtime.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What's the very first thing I should check if my air compressor won't start?
The very first thing you should check if your air compressor won't start is the power supply. This includes verifying that the unit is properly plugged in, checking the circuit breaker for any trips, inspecting fuses (if applicable) for blows, and ensuring that any emergency stop buttons are disengaged. Often, a simple power interruption or an engaged safety feature is the culprit, ruling out more complex issues immediately.
2. How can I accurately find small air leaks in my piping system?
For accurate detection of small air leaks, an ultrasonic leak detector is the most effective tool. These devices detect the high-frequency sound of escaping air, converting it into an audible signal you can hear, even over background industrial noise. For very small or difficult-to-reach leaks, applying a soapy water solution to suspected areas can reveal leaks by forming visible bubbles. Regular inspection of fittings, hoses, and connections is crucial.
3. What does it mean if my compressor is constantly running, even when no air is being used?
If your compressor is constantly running without any air being consumed, it almost always indicates a significant air leak somewhere in your distribution system. The compressor is continuously trying to compensate for the lost air. Other less common causes could include a faulty pressure switch that isn't signaling the compressor to shut off, or a malfunctioning check valve allowing air to bleed back into the compressor's air end. Prioritize a thorough leak detection audit.
4. Why is there oil in my compressed air lines, and how do I fix it?
Oil in your compressed air lines (oil carryover) is a critical issue. The most common cause is overfilling the oil reservoir. Other reasons include a clogged or faulty oil separator (in rotary screw compressors), worn piston rings or cylinder walls (in reciprocating compressors), using the incorrect type of oil, or the compressor overheating causing oil to vaporize. To fix it, first check and adjust the oil level. If the problem persists, you'll need to inspect and potentially replace the oil separator or consult a professional for internal component wear.
5. My air compressor is running hot and frequently shutting down due to thermal overload. What are the most likely causes?
Frequent thermal shutdowns and running hot typically point to issues with heat dissipation or excessive load. Most likely causes include insufficient ventilation around the compressor (it needs adequate airflow), dirty cooling fins or heat exchangers (blocking heat transfer), low oil levels or poor oil quality (leading to inadequate lubrication and cooling), high ambient temperature in the compressor room, or a clogged air intake filter forcing the compressor to work harder. Address these common causes first; if the problem persists, a professional diagnosis is warranted.
Related Articles:
Optimizing Air Compressor Longevity: Essential Maintenance Tips for Peak Performance
Air Compressor Maintenance Tips
Energy Efficiency in Air Compressors: What to Look For
The Role of CFM in Air Compressors
Don't Let Rust Rule: How to Tend to Your Air Compressor for Peak Performance
Conclusion
Mastering the art of air compressor troubleshooting is an invaluable skill for any industrial facility committed to maximizing uptime and operational efficiency. By adopting a systematic approach to diagnosing common issues like startup failures, pressure problems, excessive noise, air contamination, and overheating, you empower your team to quickly identify root causes and implement effective solutions.
Regular maintenance remains your first and best defense, but when problems inevitably arise, a clear understanding of symptoms and their corresponding fixes is paramount. Leverage the diagnostic tools at your disposal, consult your compressor's manual, and don't hesitate to engage professional expertise when the situation demands it. By being proactive and informed, you transform potential disruptions into minor setbacks, ensuring your industrial air compressor continues to reliably power your operations for years to come.
Facing persistent air compressor issues? Don't let downtime impact your productivity. This guide has equipped you with the knowledge to diagnose common problems, but sometimes you need an expert touch or specific parts to get your industrial compressor back to peak uptime.
For advanced troubleshooting support, replacement parts, or professional maintenance services, Tend Industrial Supplies is here to help. Our specialists understand the complexities of industrial air compressors and can provide the solutions you need. Email us at sales@tendsupplies.com or visit tendsupplies.com to connect with our team and ensure your operations run smoothly and efficiently.









